What Is Heel Discomfort
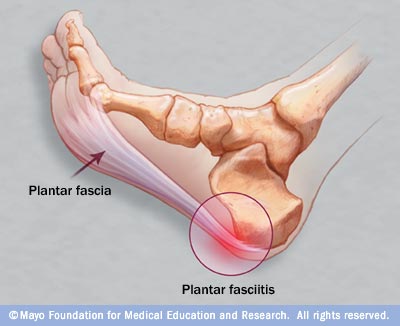
Overview
Plantar Fasciitis is actually, in most cases, plantar fasciosis but it’s a bit like pen/biro or hoover/vacuum. The term ‘-itis‘ means ‘inflammation’. This is a term we use for this problem in the early stages of damage because it usually is quite literally an inflammation of part of the plantar fascia. So, what is commonly known as ‘plantar fasciitis’ is really ‘plantar fasciosis’ - a degradation or degeneration of the collagen fibres because of prolonged (most of your adult life) unsustainable stress being applied to the fascia. So, we call it plantar fasciitis but it usually hasn’t been an ‘-itis‘ for years and that is why in many cases anti-inflammatory drugs do not help ease the pain of walking. This is also why most sufferers experience pain first thing in the morning. If inflammation was the source of discomfort then why would it hurt after a nights rest and the good old drugs pumping through your system.
Causes
Although plantar fasciitis may result from a variety of factors, such as repeat hill workouts and/or tight calves, many sports specialists claim the most common cause for plantar fasciitis is fallen arches. The theory is that excessive lowering of the arch in flat-footed runners increases tension in the plantar fascia and overloads the attachment of the plantar fascia on the heel bone (i.e., the calcaneus). Over time, the repeated pulling of the plantar fascia associated with excessive arch lowering is thought to lead to chronic pain and inflammation at the plantar fascia’s attachment to the heel. In fact, the increased tension on the heel was believed to be so great that it was thought to eventually result in the formation of a heel spur.
Symptoms
The pain associated with plantar fasciitis is typically gradual in onset and is usually located over the inner or medial aspect of the heel. Occasionally, the pain will be sudden in onset, occurring after missing a step or after jumping from a height. The pain is commonly most severe upon arising from bed in the morning, or after periods of inactivity during the day. Thus, it causes what is known as "first-step pain." The degree of discomfort can sometimes lessen with activity during the course of the day or after "warming-up", but can become worse if prolonged or vigorous activity is undertaken. The pain is also often noted to be more severe in bare feet or in shoes with minimal or no padding at the sole.
Diagnosis
After you describe your symptoms and discuss your concerns, your doctor will examine your foot. Your doctor will look for these signs. A high arch, an area of maximum tenderness on the bottom of your foot, just in front of your heel bone. Pain that gets worse when you flex your foot and the doctor pushes on the plantar fascia. The pain improves when you point your toes down. Limited "up" motion of your ankle. Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
More than 90% of patients with plantar fasciitis will improve within 10 months of starting simple treatment methods. Rest. Decreasing or even stopping the activities that make the pain worse is the first step in reducing the pain. You may need to stop athletic activities where your feet pound on hard surfaces (for example, running or step aerobics). Ice. Rolling your foot over a cold water bottle or ice for 20 minutes is effective. This can be done 3 to 4 times a day. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication. Drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen reduce pain and inflammation. Using the medication for more than 1 month should be reviewed with your primary care doctor. Exercise. Plantar fasciitis is aggravated by tight muscles in your feet and calves. Stretching your calves and plantar fascia is the most effective way to relieve the pain that comes with this condition. Cortisone injections. Cortisone, a type of steroid, is a powerful anti-inflammatory medication. It can be injected into the plantar fascia to reduce inflammation and pain. Your doctor may limit your injections. Multiple steroid injections can cause the plantar fascia to rupture (tear), which can lead to a flat foot and chronic pain. Soft heel pads can provide extra support. Supportive shoes and orthotics. Shoes with thick soles and extra cushioning can reduce pain with standing and walking. As you step and your heel strikes the ground, a significant amount of tension is placed on the fascia, which causes microtrauma (tiny tears in the tissue). A cushioned shoe or insert reduces this tension and the microtrauma that occurs with every step. Soft silicone heel pads are inexpensive and work by elevating and cushioning your heel. Pre-made or custom orthotics (shoe inserts) are also helpful. Night splints. Most people sleep with their feet pointed down. This relaxes the plantar fascia and is one of the reasons for morning heel pain. A night splint stretches the plantar fascia while you sleep. Although it can be difficult to sleep with, a night splint is very effective and does not have to be used once the pain is gone. Physical therapy. Your doctor may suggest that you work with a physical therapist on an exercise program that focuses on stretching your calf muscles and plantar fascia. In addition to exercises like the ones mentioned above, a physical therapy program may involve specialized ice treatments, massage, and medication to decrease inflammation around the plantar fascia. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT). During this procedure, high-energy shockwave impulses stimulate the healing process in damaged plantar fascia tissue. ESWT has not shown consistent results and, therefore, is not commonly performed. ESWT is noninvasive-it does not require a surgical incision. Because of the minimal risk involved, ESWT is sometimes tried before surgery is considered.

Surgical Treatment
Most patients have good results from surgery. However, because surgery can result in chronic pain and dissatisfaction, it is recommended only after all nonsurgical measures have been exhausted. The most common complications of release surgery include incomplete relief of pain and nerve damage.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching your plantar fasciitis is something you can do at home to relieve pain and speed healing. Ice massage performed three to four times per day in 15 to 20 minute intervals is also something you can do to reduce inflammation and pain. Placing arch supports in your shoes absorbs shock and takes pressure off the plantar fascia.